[% INCLUDE header.us3/
title = 'UltraScan III Time Derivative (dC/dt) Data Analysis'
%]
UltraScan Time Derivative (dC/dt) Data Analysis:
The DCDT or Time Derivative method will calculate g(S) differential
sedimentation profiles by subtracting consecutive scan pairs from each
other and mapping the resulting difference curves to the S domain to
obtain dcdt curves. The advantage of this method is its ability to nicely
subtract out time invariant noise, such as window scratches and dirt,
as well as refractive index hetereogeneities in the windows. The latter
is particularly important for low-concentration interference data. Unlike
the van Holde - Weischet method, the Time
Derivative method does not correct for diffusion. In order to obtain
accurate results with this method, it is important that you use only a
small scan range over which diffusion has not changed significantly.
-
Load Experiment Click on this button and, in the resulting
Load Data Dialog, select an edited
data set to load.
-
Run Details Bring up a dialog with a summary of data
and run details.
-
Latest Data Edit Uncheck to allow choosing an edit other
than the latest one for the experimental data.
-
Database Check to specify data input from the database.
-
Local Disk Check to specify data input from local disk.
-
View Data Report Create a results text file and display
its contents in a text dialog.
-
Save Data Create several data and report files based on
input data and vHW parameters.
-
Run ID / Edit ID: The main run title of the data and
an edit identifier are displayed.
-
Avg Temperature: The average temperature of solute is
displayed in Celsius.
-
(description) The text box below the one for temperature
shows a full data description string.
-
Cell / Channel / Wavelength The text box below this label
gives cell, channel and wavelength triples available in this
data set. Highlight the desired value.
-
Solution Click this button to open a
Solution Management dialog
that allows changes to buffer and analyte characteristics of
the data set.
-
Density (20° C) Shows the density value for the loaded
experiment. Click the Solution button to open a dialog in which
density and other values may be changed.
-
Viscosity (20° C) Shows the viscosity value for thes
loaded experiment. Click the Solution button to open a dialog
in which viscosity and other values may be changed.
-
Vbar (20° C) Shows the vbar value for the loaded
experiment. Click the Solution button to open a dialog in
which vbar and other values may be changed.
-
Skipped The count of experiment data scans skipped.
-
Scan focus from: Choose the first of a range of scan numbers
that may potentially be excluded from analysis.
-
To: Choose the end of a range of scan numbers that may
potentially be excluded from analysis. The From/To scan range
is illustrated in both plots to the right.
-
Exclude Scan Range If the From/To scan range selections
are as desired, click on this button to exclude the indicated
scans from analysis.
-
Reset Scan Range Reset to the full range of scans.
-
Data Smoothing: Choose the number of points to use for
any smoothing of raw input data.
-
Boundary Pos. (%): Choose the percent of the
plateau-baseline range that is to be added to the baseline to
form the beginning of analysis span.
-
S-value Cutoff: Choose the sedimentation coefficient
value to form the maximum X value of the Time Derivative plot.
-
x:radius Select this radio button to choose a
g*(S) versus radius dC/dt plot.
-
x:S Select this radio button to choose a
g*(S) versus sedimentation coefficient dC/dt plot.
-
Average S Select this radio button to choose an
Average g*(S) versus sedimentation coefficient dC/dt plot.
-
Reset Indicate that parameters are to be reset and the
plots re-displayed based on original parameters.
-
Help Display this detailed Time-Derivative help.
-
Close Close all windows and exit.
-
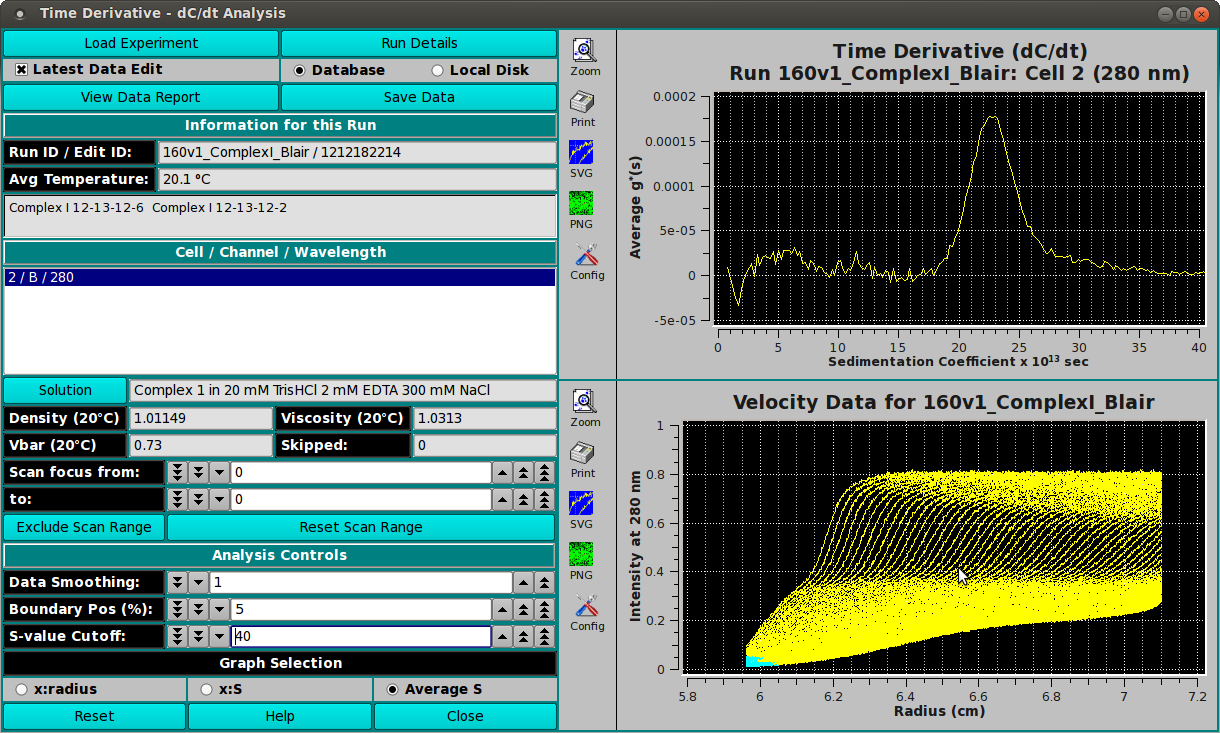
(Time Derivative Plot) The upper of the two right-side plots
shows one of three types (x:radius, x:S, Average S) of
Time Derivative (dC/dt) plots.
-
(Velocity Data Plot) The lower of the right-side plots
shows selected velocity data for which a time derivative
calculation has been made.
[% INCLUDE footer.us3 %]
 Manual
Manual
 Manual
Manual
